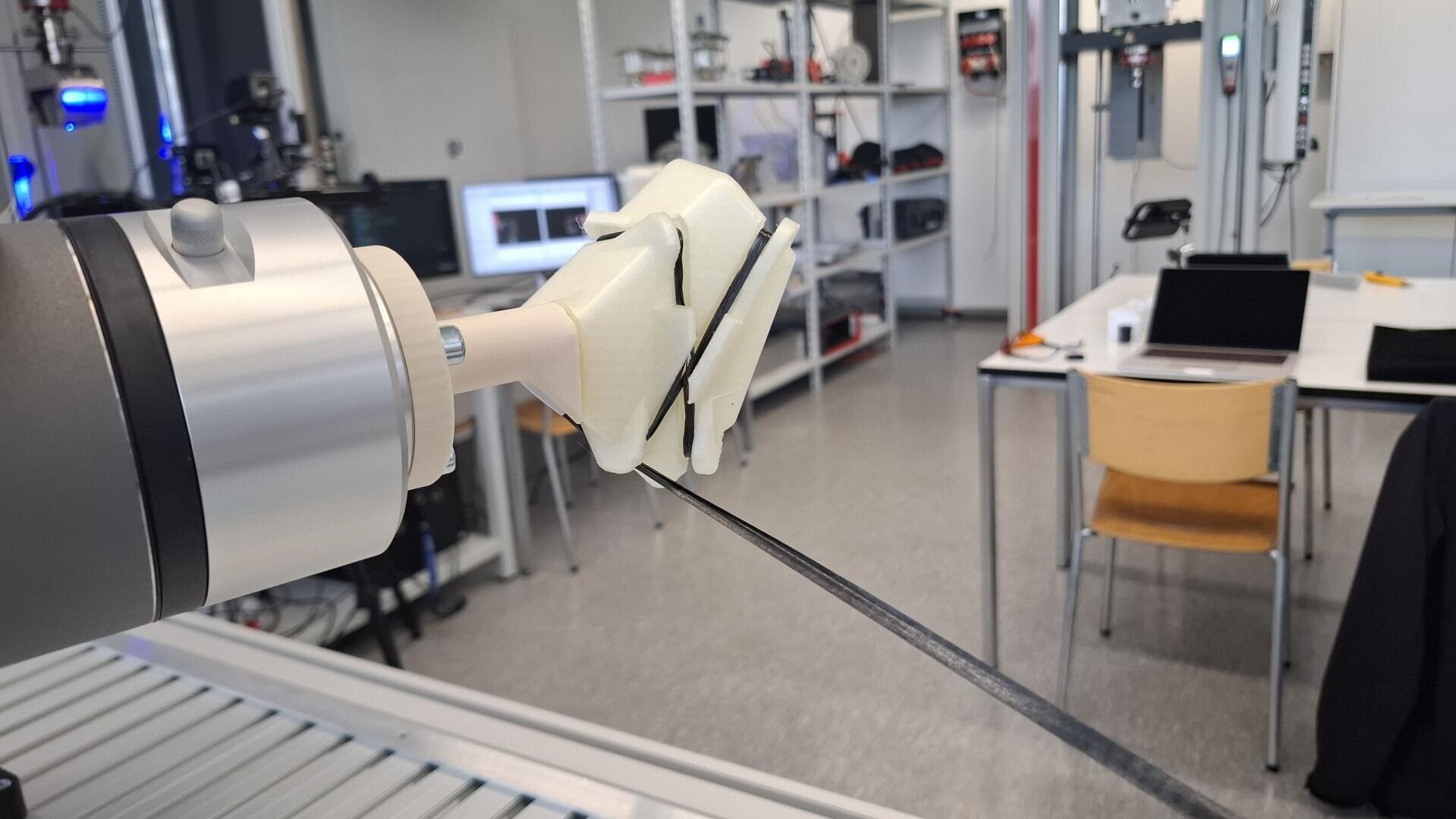
Additive fibre composite structures: New possibilities through robot-assisted 3D fiber winding
With a newly developed manufacturing process, the ZHAW School of Engineering shows how topology-optimised fibre composite components can be produced efficiently and with high precision.
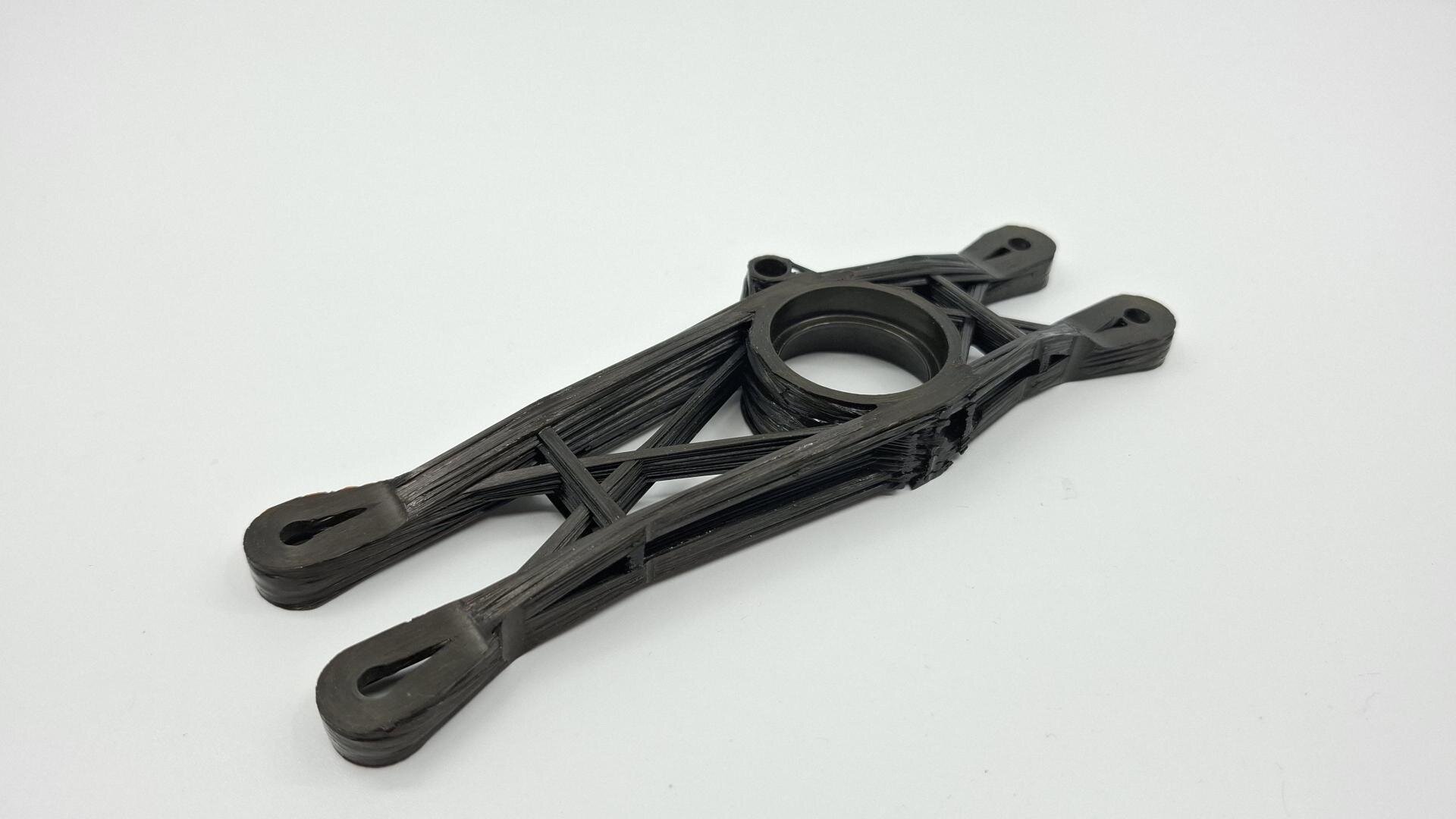
The so-called “3D fibre winding” allows the automated deposition of reinforcing fibres along ideal load paths – even for complex 3D components.
At the heart of the process is a cobot that deposits continuous rovings along guiding channels on an additively manufactured winding tool. This creates truss-like structures that are characterized by extreme lightweight performance. Compared to a milled aluminum component, the weight of an aircraft component could be more than halved while increasing the specific stiffness by 160 %.
Thanks to the high degree of automation, material waste is minimal, and reproducibility is high – a promising approach for lightweight components in aerospace and mechanical engineering. The method closes an important gap between traditional 2D laminates and complex, often inflexible 3D fibre laying technologies.